In this blog post, you will learn how to work with Qorus in Docker.
docker --version. Qorus Integration Engine(R) Community Edition Docker Images
Qore Technologies offers three docker images for the Community Edition, one based on Ubuntu, and two based on Alpine Linux. All Community Edition images are multi-arch images, supporting amd64 (x86_64) and arm64 (aarch64) processors. For details on each image, see Qorus Images in the Elastic Container Registry
| Docker Images | Features |
|---|---|
| public.ecr.aws/qorus/qorus-ce:latest | based on Ubuntu with Java, Python, Oracle libraries + Firebird ODBC drivers |
| public.ecr.aws/qorus/qorus-ce-alpine:latest | based on Alpine Linux with Java, Python, Oracle libraries |
| public.ecr.aws/qorus/qorus-ce-alpine-minimal:latest | based on Alpine Linux with Python but without Java or Oracle client libraries |
Qorus Integration Engine(R) Enterprise Edition Docker Images
Qore Technologies offers four docker images for the Enterprise Edition, two based on Ubuntu, and two based on Alpine Linux. As of Qorus v5.1+, all four images are multi-arch images, supporting amd64 (x86_64) and arm64 (aarch64) processors. For details on each image, see Qorus Images in the Elastic Container Registry
| Docker Images | Features |
|---|---|
| public.ecr.aws/qorus/qorus-ee:latest | based on Ubuntu with Java, Python, Oracle libraries + Firebird ODBC drivers |
| public.ecr.aws/qorus/qorus-ee-go:latest | qorus:latest + go and grpcurl |
| public.ecr.aws/qorus/qorus-ee-alpine:latest | based on Alpine Linux with Java, Python, Oracle libraries |
| public.ecr.aws/qorus/qorus-ee-alpine-minimal:latest | based on Alpine Linux with Python but without Java or Oracle client libraries |
Running Qorus In a Docker Container
git clone https://github.com/qoretechnologies/qorus-docker.git2. Change directory to the Community Edition directory in the repository.
cd qorus-docker/qorus-ce
qorus-ee to start the Enterprise Edition
3. Use Docker compose to pull and run Qorus in a Docker container.
docker-compose up -dUnderstanding Docker Configuration and Organisation
The Docker configuration and organization is dictated by the docker-compose.yml file when you run ‘docker-compose up -d‘. In this section, you will understand the docker-compose.yml file and how each of the elements in this file affect Docker’s configuration.
Services
The service element is a root element of any compose file. A service definition contains the configuration that is applied to each container started for that service. You will find the following service definitions inside the docker-compose.yml file.
qorus:
image: public.ecr.aws/qorus/qorus-ce:latest
ports:
- "8011:8011"
environment:
OMQ_DB_NAME: postgres
OMQ_DB_TYPE: pgsql
OMQ_DB_HOST: pg
OMQ_DB_USER: postgres
OMQ_DB_PASS: omq
TZ: Europe/Prague
restart: always
volumes:
- ./qorus-etc:/opt/qorus/etc
- ./qorus-log:/opt/qorus/log
- ./qorus-user:/opt/qorus/user
links:
- pg
ulimits:
nproc:
soft: 8192
hard: 65536
nofile:
soft: 8192
hard: 32768 pg:
image: postgres:15
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: omq
TZ: Europe/Prague
PGTZ: Europe/Prague
volumes:
- ./qorus-postgres-data:/var/lib/postgresql/datadocker-compose.yml file includes a service definition to set up a database. The database files are also mounted from a Docker volume in order to make the database persistent. Service Definitions
image
The ‘image’ element specifies the image to start the container from. In the compose file above, the image element is set to a Qorus image based on Ubuntu Jammy Jellyfish – 22.04 LTS (public.ecr.aws/qorus/qorus-ce:latest)
ports
The ports element exposes container ports. It follows the following format host_post:container_port.
ports:
- "8011:8011"In this example, the ports attribute exposes the Qorus instance on the local port 8011. To expose the Qorus instance on another local port, say, 10011 change the port attribute to “10011:8011”. This will open up the Qorus instance on the local port 10011.
environment
The environment element defines environment variables set in the container. This is one of the ways to configure Qorus’s system DB. In the present scenario we have the following
environment:
OMQ_DB_NAME: postgres
OMQ_DB_TYPE: pgsql
OMQ_DB_HOST: pg
OMQ_DB_USER: postgres
OMQ_DB_PASS: omq
TZ: Europe/PragueThe OMQ_DB_PASS is the password to the PostgreSQL image’s database. Ensure that its value matches the password set for the PostgreSQL image above.
The TZ environment variable will set the time zone for the Qorus container. Make sure you use a valid timezone name.

restart
The restart attribute configures the behaviour when the container exits, whether it be through an error, a normal exit etc. Since we usually want Qorus to run constantly, we set it to ‘always‘.
volumes
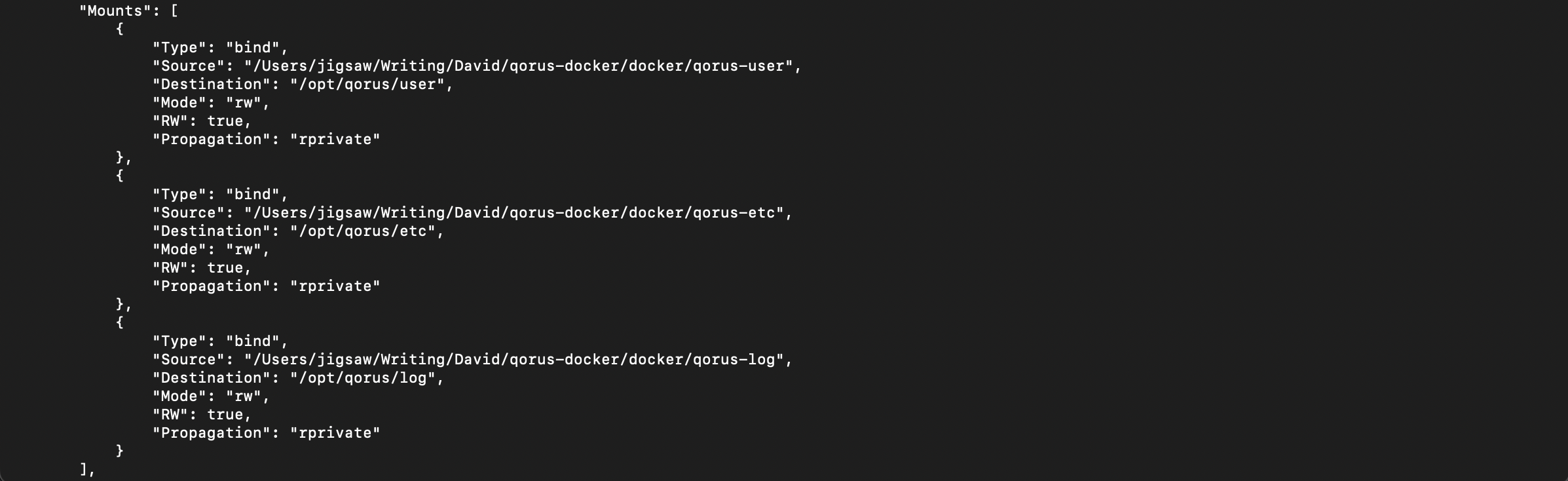
“volumes” mount host filesystem directories into the container. This is necessary to run Qorus and its database with persistent data. It follows the format VOLUME:CONTAINER:PATH. With the above attributes under the volume element, Docker will create three docker volumes – ‘qorus-etc‘, ‘qorus-log‘, and ‘qorus-user‘ on the host to which the container’s data is written for persistence. With Docker, the volume names will be prefixed with ‘docker_,‘ so on the host machine, the volumes will be as follows:

On the container, these volumes are mapped to the keys specified in the volumes element. i.e., to the ‘/opt/qorus/etc‘, ‘/opt/qorus/log‘ and ‘/opt/qorus/user‘ directories.
| Qorus Volume | Mapped Directory in the Container | Description | Host Machine Mounts |
|---|---|---|---|
| qorus-etc | /opt/qorus/etc | The OMQ_DIR/etc directory is dedicated to storing the system configuration files. The system and client options can be set through the 'options' file contained in this directory. Here is a list of all the system options in the qorus option domain. | (compose file directory)/qorus-etc |
| qorus-log | /opt/qorus/log | The OMQ_DIR/log directory is for the the Qorus' runtime logs. Log file names are created based on template strings that undergo variable substitution. | (compose file directory)/qorus-log |
| qorus-user | /opt/qorus/user | The OMQ_DIR/user directory is for the Qorus user definition files, code objects, interface descriptions, release source. | (compose file directory)/qorus-user |
| qorus-postgres-data | /var/lib/postgresql/data | PostgreSQL 15 database for Qorus with a persistent volume for the database files | (compose file directory)/qorus-postgres-data |
To get more information and to verify that the volumes were created and mounted correctly, run docker inspect container id and go the “Mounts” array.
links
links defines a network link to containers in another service. In the present scenario we link the PostgreSQL service in the Qorus service definition. This isn’t strictly necessary as Qorus can work with any supported database (PostgreSQL, MariaDB/MySQL, or Oracle) accessible from the network, however in this case to you need to set environment variables appropriately to connect to the local database. Additionally, in this case, the DB must already exist, and the DB user must have permissions to create all the required DB objects in the schema.
Ulimits / Resource Limits
ulimit is a Linux shell command used to monitor and control the resource usage of the current user. The user running Qorus Integration Engine must have minimum hard and soft limits for the number of descriptors available (nofile) and the number of processes and threads (nproc). In the compose file, above
ulimits:
nproc:
soft: 8192
hard: 65536
nofile:
soft: 8192
hard: 32768The soft limits for both, nproc and nofile are set to 8192 which is the recommended value for Qorus.
Running Qorus in Docker Manually
1. Pull the Qorus Docker image with:
docker pull public.ecr.aws/qorus/qorus-ce:latestdocker pull postgres:153. Start the DB container first
docker run —name pg -v $HOME/qorus/postgresql-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=omq -e TZ=Europe/Prague -e
PGTZ=Europe/Prague -d postgres:154. Create persistent directories for Qorus:
mkdir -p $HOME/qorus/etc $HOME/qorus/user $HOME/qorus/log5. Download and start the Qorus image in a Docker container:
docker run --name qorus \ --link pg:postgres \ --restart always -p 8011:8011 \ --ulimit nofile=8192:8192 \ --ulimit nproc=8192:8192 \ -e OMQ_DB_NAME=postgres \ -e OMQ_DB_TYPE=pgsql \ -e OMQ_DB_HOST=postgres \ -e OMQ_DB_USER=postgres \ -e OMQ_DB_PASS=omq \ -e TZ=Europe/Prague \ -e QORUS_ADMIN_PASS=changeme \ -e QORUS_UID=1000 \ -e QORUS_GID=100 \ -v $HOME/qorus/qorus-etc:/opt/qorus/etc \ -v $HOME/qorus/qorus-log:/opt/qorus/log \ -v $HOME/qorus/qorus-user:/opt/qorus/user \ -d public.ecr.aws/qorus/qorus-ce:latest
Executing Qorus commands in the Docker container
Docker commands can be executed in the Docker container directly from the host container with:
docker exec [container-id] bash -l -c "[command]"Example, to get a list of all the Qorus services, run – docker exec [container-id] bash -l -c “qctl ps”.To get the container-id run “docker ps“.

Getting Docker container's shell
To get a docker container’s shell, in the host machine, run:
docker exec -it [container-id] bash -lEnabling RBAC in The Container (Enterprise Edition Only)
RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) is only supported in the Enterprise Edition and cannot be enabled in the Community Edition, however it is disabled by default in a new Docker instance of Qorus Enterprise Edition. To enable it in the Enterprise Edition of Qorus, edit the qorus-etc/options file on the host ($OMQ_DIR/etc/options) file in the container and enable/uncomment the qorus.rbac-security option in the file:
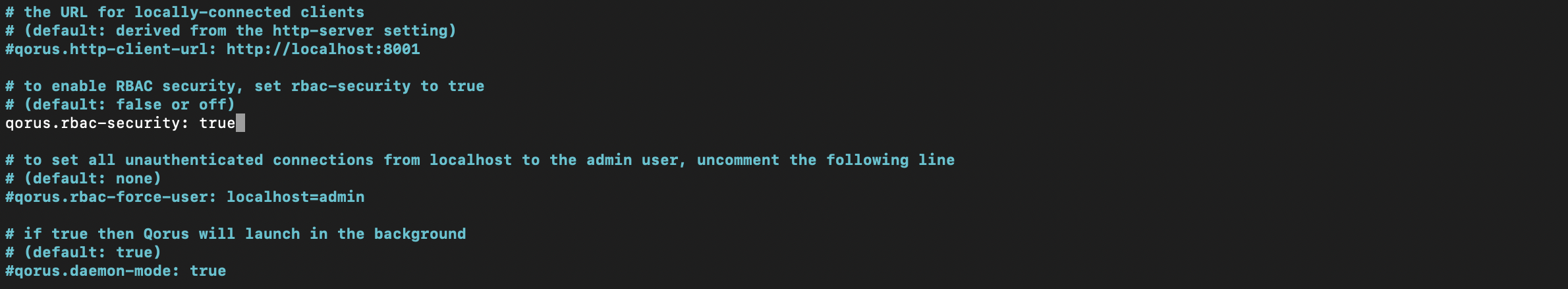
Then restart qorus
With manual docker configuration, in the host, run:
docker restart [qorus-container-name]
With Docker compose, in the directory containing the cocker-compose.yml file, run:
docker-
Qorus Admin Account (Enterprise Edition Only)
The Community Edition of Qorus does not support users and permissions and has no admin account. This section applies only to Qorus Enterprise Edition.
If the QORUS_ADMIN_PASS environment variable is set when the Docker container is started for the first time, the account password will be set to the value of this environment variable.
If no password environment variables were set, then the random string used to set the admin user’s password is logged in the output during the container’s initialization.
To reset the admin password on subsequent runs of the Docker container, set FORCE_UPDATE_ADMIN_USER=1 and restart the container
Updating Qorus with a new image
1. From a manual Docker configuration
- docker stop [qorus-container-name]
- docker rm [qorus-container-name]
- docker pull [image name]
- docker run –name …
2. With Docker Compose from the directory with the docker-compose.yml file
- docker-compose up –force-recreate –build -d

